BPA stands for Bisphenol A, an organic compound with the molecular formula C15H16O2. It is a colorless solid substance that is soluble in organic solvents, but insoluble in water. That’s why when you put it in a hot or cold drink, chemicals can leach into the drink. To make sure you can drink non-toxic water, there is a way (recycling codes) to test your bottle for BPA-free.
Check The Recycling Codes
If you’re looking at a plastic bottle or jar at home and wondering if it’s BPA-free, follow these steps:
First, you should check the outer packaging, which usually states whether the product is BPA-free. Check the product or packaging for the manufacturer’s description, such as a BPA-free sticker or label.
The most reliable way to check whether an item is BPA-free is to consult the plastic identification code number — usually stamped on the bottom of the container.
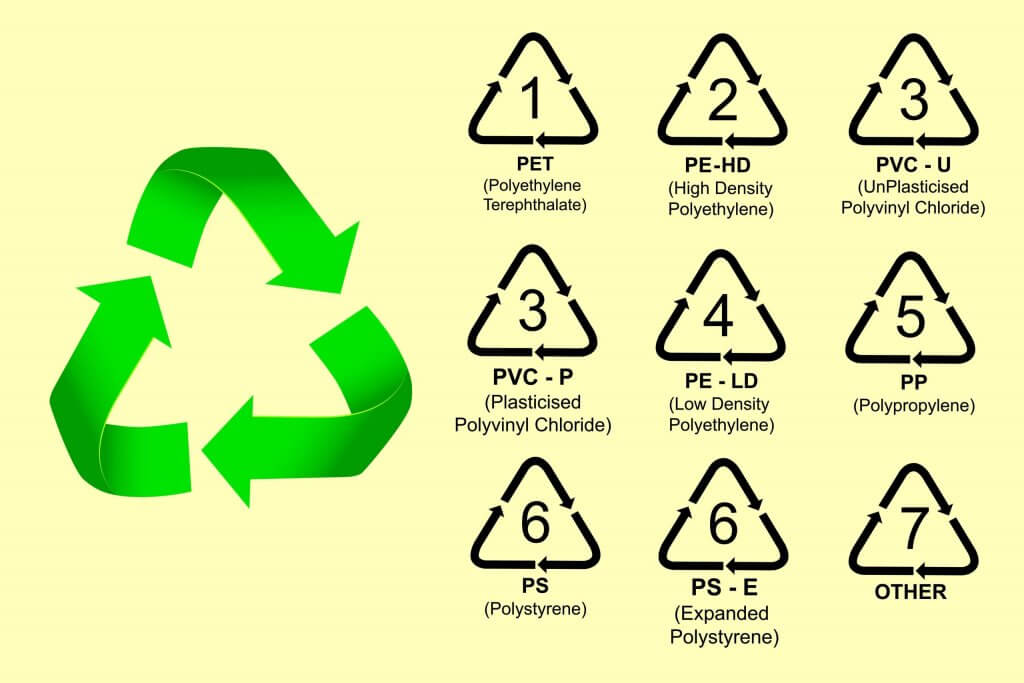
Turn the bottle upside down and look for the plastic resin identification code (often called a recycling code) on the bottom. The symbol has a number (from 1 to 7) surrounded by three chasing arrows shaped like a triangle.
| Number | Code Letter(s) | Name of plastic or resin | Examples of use |
| 1 | PETE / PET | Polyethylene terephthalate | Soft drinks bottles |
| 2 | HDPE | High-density polyethylene | Some reusable plastic food storage containers |
| 3 | V / PVC | Vinyl or polyvinyl chloride | Debit and credit cards |
| 4 | LDPE | Low-density polyethylene | Plastic shopping bags |
| 5 | PP | Polypropylene | Some reusable plastic food storage containers |
| 6 | PS | Polystyrene | Foam drinking cups |
| 7 | OTHER | Other substances (may include BPA) | Any item not made of the above materials |
recycling codes: Code 1 PET
The scientific name of polyethylene terephthalate is also referred to as polyester plastic. It’s common in life, the current beverage bottles and food oil bottles are almost all used in this plastic. If the molecular weight of PET is large enough, it can be used in the fiber industry.
recycling codes: Code 2 HDPE
High-density polyethylene is the easiest to find in your bathroom as a chemical container and is also used in many large beverage bottles. Different from PET, HDPE is highly crystalline, so it appears opaque and harder, even a little brittle. Because of its high strength, fall resistance, and imperviousness to light, daily products often use plastic No. 2.
recycling codes: Code 3 PVC
Also known as polyvinyl chloride, is the only one of the seven plastics not BPA-safe and not recommended for contact with food because it contains chlorine. In fact, the chlorine in the material is not easily dissociated under normal conditions of use, although No. 3 plastic is rarely seen in food containers. PVC is also the only one of the seven plastics that must use a plasticizer, which allows it to change its state from soft and elastic to hard and brittle.
recycling codes: Code 4 LDPE
Plastic No. 4 HDPE and plastic No. 2 are brothers, technically called low-density polyethylene. But essentially 2 and 4 have different structures, except that the monomers are all ethylene. HDPE’s transparency is relatively high, so we can mainly see it in plastic wrap, plastic bags, and other aspects of our daily lives.
recycling codes: Code 5 PP
PP is our star plastic polypropylene, the most common than the button. At present, the vast majority of microwave oven special plastic containers on the market are PP plastic, because their heat resistance and chemical stability are higher. This kind of plastic is actually very close to No.2 plastic, crystallinity is lower than No.2 slightly, it’s translucent state commonly, the hardness with No.2 differs not too much. This is a food-safe material, as polypropylene doesn’t contain BPA.
recycling codes: Code 6 PS
There was a time when plastic No. 6 was everywhere, especially on both sides of Chinese railways, but nearly 20 years later, many people have forgotten the “white pollution”.
Up to now, the important use of No.6 plastic is still foamed plastic, the polystyrene board in the home decoration refers to this kind of plastic, but in the food aspect the status is reduced a lot, generally, in the instant noodles, the family bucket of these food packaging is still widely used, foam lunch box of course, but many people will refuse to use.
recycling codes: Code 7 OTHER
No. 7 plastic PC is not a PC, it’s polycarbonate, but it has to do with PCS, and a lot of them are PC plastic. Some places say that Number 7 stands for “other plastic,” which is true, but because of the widespread use of PCS, number 7 is now basically equivalent to polycarbonate plastic.
In conclusion:
- If you see 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 recycling codes, you can safely assume that the bottle is BPA-free.
- If it is 3 or PVC, it may contain BPA. PVC is no longer used in most food and beverage containers, and its use as a food lining material for metal cans is declining.
- If you see 7, you will not be able to tell if it contains BPA, as 7 is considered the “all-in-one” category into which all other plastic resins fall. If you know that a plastic bottle is made of PVC material, then it contains BPA.
Where To Buy Wholesale BPA-Free Bottles
Everich BPA-free water bottles have similar weight and durability to conventional plastic, and unlike the inexpensive resins used by many other companies to make BPA-free water bottles, our BPA-free water bottles do not crack or rupture when dropped. Our materials available are plastic like PP, PC, Tritan, SK, Petg, acrylic, PCTG, AS, and so on. They are 100% BPA-free, 100% food-safe grade, compliant with European and American food-safe standards, and passed third-party tests such as FDA, LFGB, and EC1935-24.
The MOQ of plastic water bottles is 500 – 3000 pieces, and the mold opening and production period are basically about 30 days. If you want to begin your sports water bottle business, send us an inquiry today!




